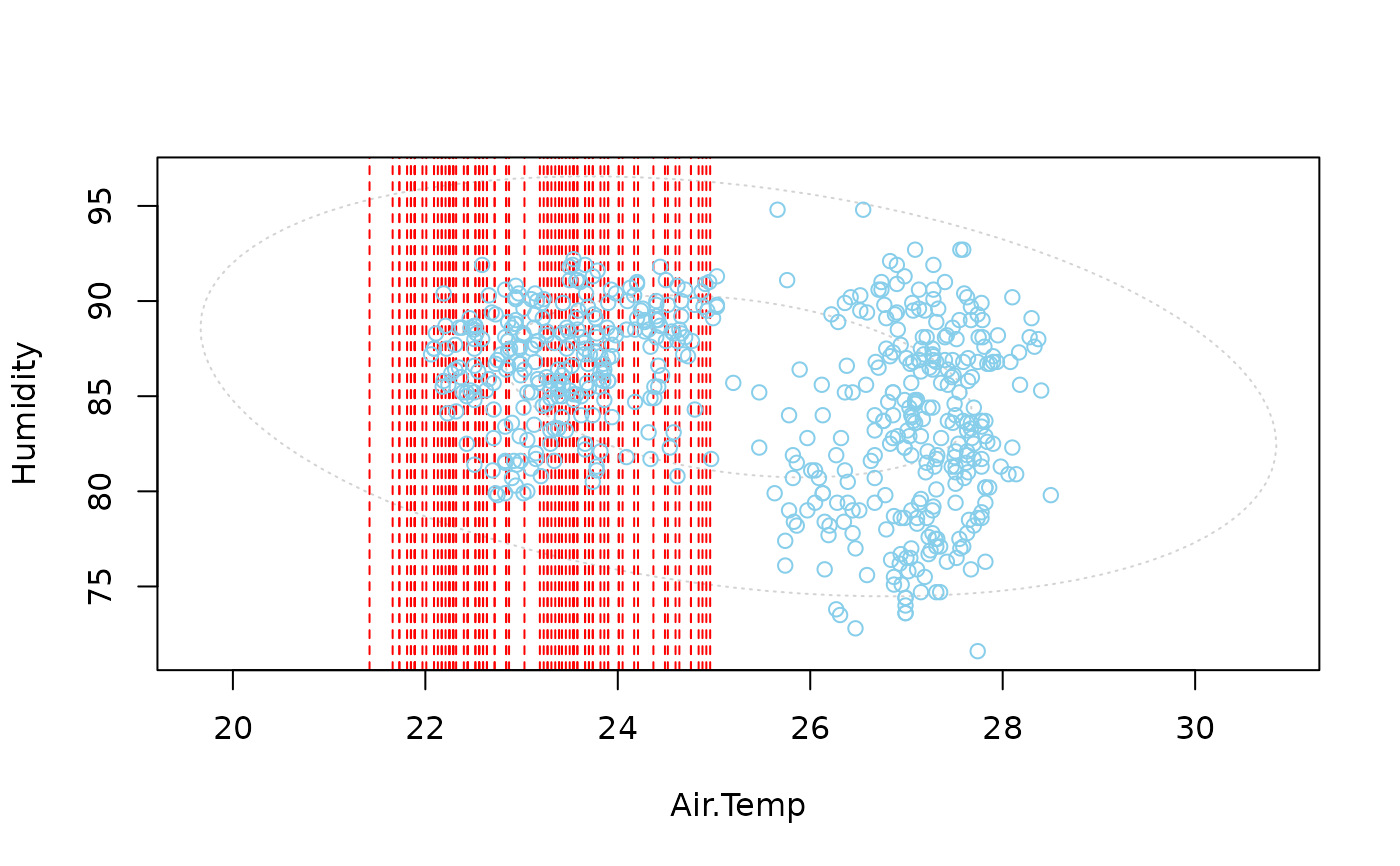
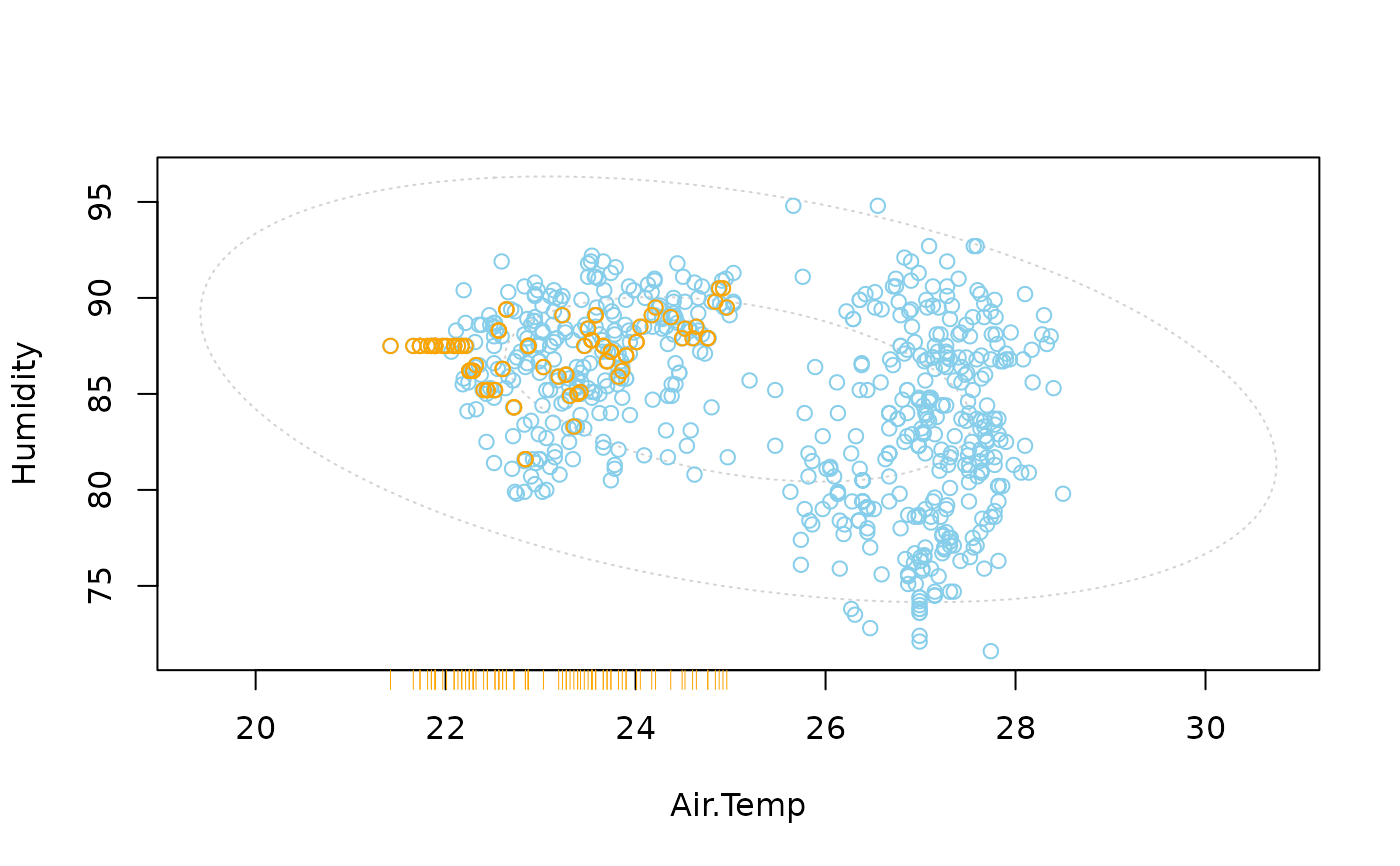
In addition to a standard scatterplot, lines are plotted for the missing values in one variable. If there are imputed values, they will be highlighted.
scattMiss(
x,
delimiter = NULL,
side = 1,
col = c("skyblue", "red", "orange", "lightgrey"),
alpha = NULL,
lty = c("dashed", "dotted"),
lwd = par("lwd"),
quantiles = c(0.5, 0.975),
inEllipse = FALSE,
zeros = FALSE,
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
main = NULL,
sub = NULL,
xlab = NULL,
ylab = NULL,
interactive = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- x
a
matrixordata.framewith two columns.- delimiter
a character-vector to distinguish between variables and imputation-indices for imputed variables (therefore,
xneeds to havecolnames()). If given, it is used to determine the corresponding imputation-index for any imputed variable (a logical-vector indicating which values of the variable have been imputed). If such imputation-indices are found, they are used for highlighting and the colors are adjusted according to the given colors for imputed variables (seecol).- side
if
side=1, a rug representation and vertical lines are plotted for the missing/imputed values in the second variable; ifside=2, a rug representation and horizontal lines for the missing/imputed values in the first variable.- col
a vector of length four giving the colors to be used in the plot. The first color is used for the scatterplot, the second/third color for the rug representation for missing/imputed values. The second color is also used for the lines for missing values. Imputed values will be highlighted with the third color, and the fourth color is used for the ellipses (see ‘Details’). If only one color is supplied, it is used for the scatterplot, the rug representation and the lines, whereas the default color is used for the ellipses. Else if a vector of length two is supplied, the default color is used for the ellipses as well.
- alpha
a numeric value between 0 and 1 giving the level of transparency of the colors, or
NULL. This can be used to prevent overplotting.- lty
a vector of length two giving the line types for the lines and ellipses. If a single value is supplied, it will be used for both.
- lwd
a vector of length two giving the line widths for the lines and ellipses. If a single value is supplied, it will be used for both.
- quantiles
a vector giving the quantiles of the chi-square distribution to be used for the tolerance ellipses, or
NULLto suppress plotting ellipses (see ‘Details’).- inEllipse
plot lines only inside the largest ellipse. Ignored if
quantilesisNULLor if there are imputed values.- zeros
a logical vector of length two indicating whether the variables are semi-continuous, i.e., contain a considerable amount of zeros. If
TRUE, only the non-zero observations are used for computing the tolerance ellipses. If a single logical is supplied, it is recycled. Ignored ifquantilesisNULL.- xlim, ylim
axis limits.
- main, sub
main and sub title.
- xlab, ylab
axis labels.
- interactive
a logical indicating whether the
sideargument can be changed interactively (see ‘Details’).- ...
further graphical parameters to be passed down (see
graphics::par()).
Details
Information about missing values in one variable is included as vertical or
horizontal lines, as determined by the side argument. The lines are
thereby drawn at the observed x- or y-value. In case of imputed values, they
will additionally be highlighted in the scatterplot. Supplementary,
percentage coverage ellipses can be drawn to give a clue about the shape of
the bivariate data distribution.
If interactiveis TRUE, clicking in the bottom margin redraws
the plot with information about missing/imputed values in the first variable
and clicking in the left margin redraws the plot with information about
missing/imputed values in the second variable. Clicking anywhere else in
the plot quits the interactive session.
Note
The argument zeros has been introduced in version 1.4. As a
result, some of the argument positions have changed.
References
M. Templ, A. Alfons, P. Filzmoser (2012) Exploring incomplete data using visualization tools. Journal of Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, Online first. DOI: 10.1007/s11634-011-0102-y.
See also
Other plotting functions:
aggr(),
barMiss(),
histMiss(),
marginmatrix(),
marginplot(),
matrixplot(),
mosaicMiss(),
pairsVIM(),
parcoordMiss(),
pbox(),
scattJitt(),
scattmatrixMiss(),
spineMiss()