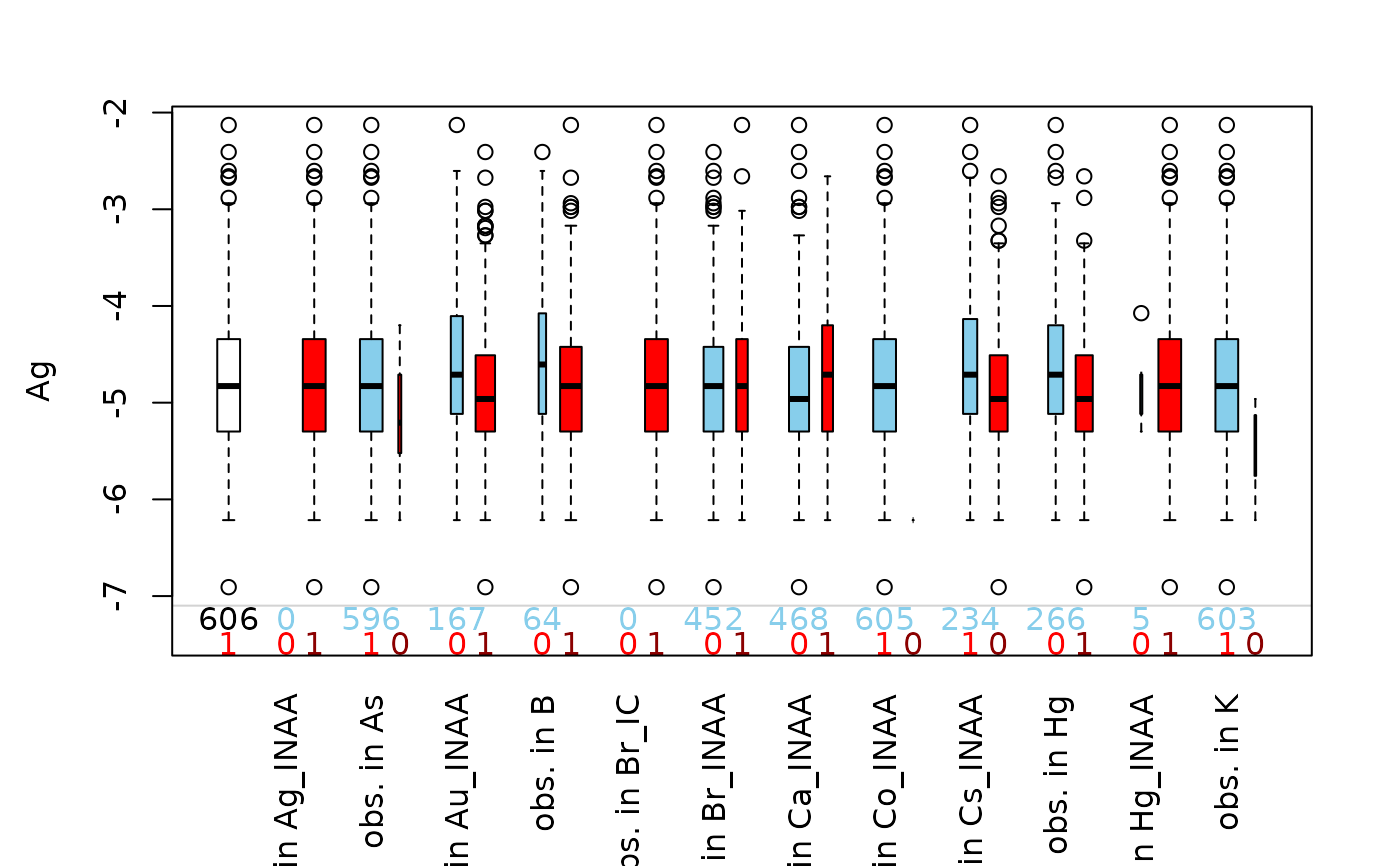
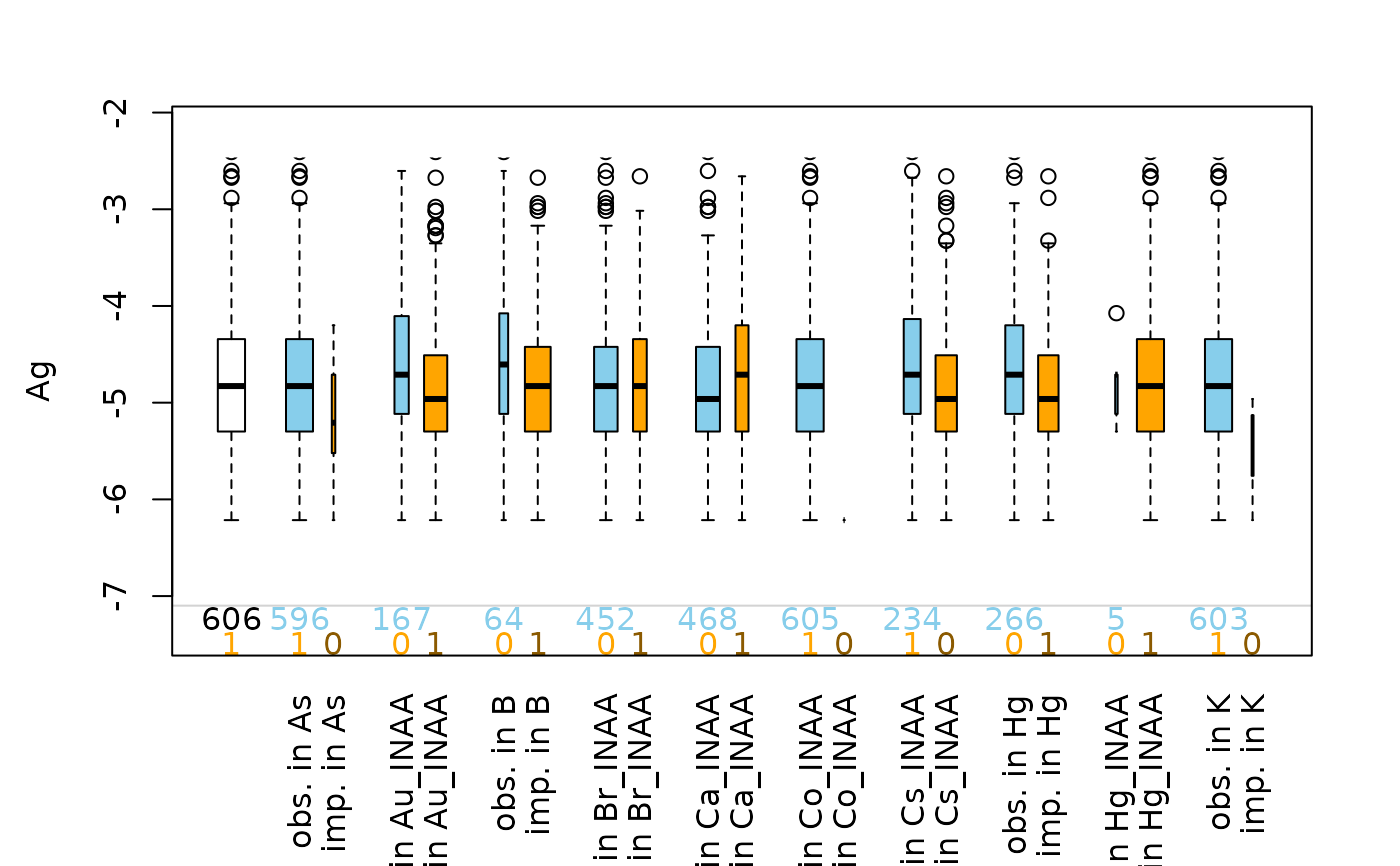
Boxplot of one variable of interest plus information about missing/imputed values in other variables.
pbox(
x,
delimiter = NULL,
pos = 1,
selection = c("none", "any", "all"),
col = c("skyblue", "red", "red4", "orange", "orange4"),
numbers = TRUE,
cex.numbers = par("cex"),
xlim = NULL,
ylim = NULL,
main = NULL,
sub = NULL,
xlab = NULL,
ylab = NULL,
axes = TRUE,
frame.plot = axes,
labels = axes,
interactive = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- x
a vector, matrix or
data.frame.- delimiter
a character-vector to distinguish between variables and imputation-indices for imputed variables (therefore,
xneeds to havecolnames()). If given, it is used to determine the corresponding imputation-index for any imputed variable (a logical-vector indicating which values of the variable have been imputed). If such imputation-indices are found, they are used for highlighting and the colors are adjusted according to the given colors for imputed variables (seecol).- pos
a numeric value giving the index of the variable of interest. Additional variables in
xare used for grouping according to missingness/number of imputed missings.- selection
the selection method for grouping according to missingness/number of imputed missings in multiple additional variables. Possible values are
"none"(grouping according to missingness/number of imputed missings in every other variable that contains missing/imputed values),"any"(grouping according to missingness/number of imputed missings in any of the additional variables) and"all"(grouping according to missingness/number of imputed missings in all of the additional variables).- col
a vector of length five giving the colors to be used in the plot. The first color is used for the boxplots of the available data, the second/fourth are used for missing/imputed data, respectively, and the third/fifth color for the frequencies of missing/imputed values in both variables (see ‘Details’). If only one color is supplied, it is used for the boxplots for missing/imputed data, whereas the boxplots for the available data are transparent. Else if two colors are supplied, the second one is recycled.
- numbers
a logical indicating whether the frequencies of missing/imputed values should be displayed (see ‘Details’).
- cex.numbers
the character expansion factor to be used for the frequencies of the missing/imputed values.
- xlim, ylim
axis limits.
- main, sub
main and sub title.
- xlab, ylab
axis labels.
- axes
a logical indicating whether axes should be drawn on the plot.
- frame.plot
a logical indicating whether a box should be drawn around the plot.
- labels
either a logical indicating whether labels should be plotted below each box, or a character vector giving the labels.
- interactive
a logical indicating whether variables can be switched interactively (see ‘Details’).
- ...
for
pbox, further arguments and graphical parameters to be passed tographics::boxplot()and other functions. ForTKRpbox, further arguments to be passed topbox.
Value
a list as returned by graphics::boxplot().
Details
This plot consists of several boxplots. First, a standard boxplot of the
variable of interest is produced. Second, boxplots grouped by observed and
missing/imputed values according to selection are produced for the
variable of interest.
Additionally, the frequencies of the missing/imputed values can be represented by numbers. If so, the first line corresponds to the observed values of the variable of interest and their distribution in the different groups, the second line to the missing/imputed values.
If interactive=TRUE, clicking in the left margin of the plot results
in switching to the previous variable and clicking in the right margin
results in switching to the next variable. Clicking anywhere else on the
graphics device quits the interactive session.
Note
Some of the argument names and positions have changed with version 1.3
due to extended functionality and for more consistency with other plot
functions in VIM. For back compatibility, the arguments names
and cex.text can still be supplied to ...{} and are handled
correctly. Nevertheless, they are deprecated and no longer documented. Use
labels and cex.numbers instead.
References
M. Templ, A. Alfons, P. Filzmoser (2012) Exploring incomplete data using visualization tools. Journal of Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, Online first. DOI: 10.1007/s11634-011-0102-y.
See also
Other plotting functions:
aggr(),
barMiss(),
histMiss(),
marginmatrix(),
marginplot(),
matrixplot(),
mosaicMiss(),
pairsVIM(),
parcoordMiss(),
scattJitt(),
scattMiss(),
scattmatrixMiss(),
spineMiss()