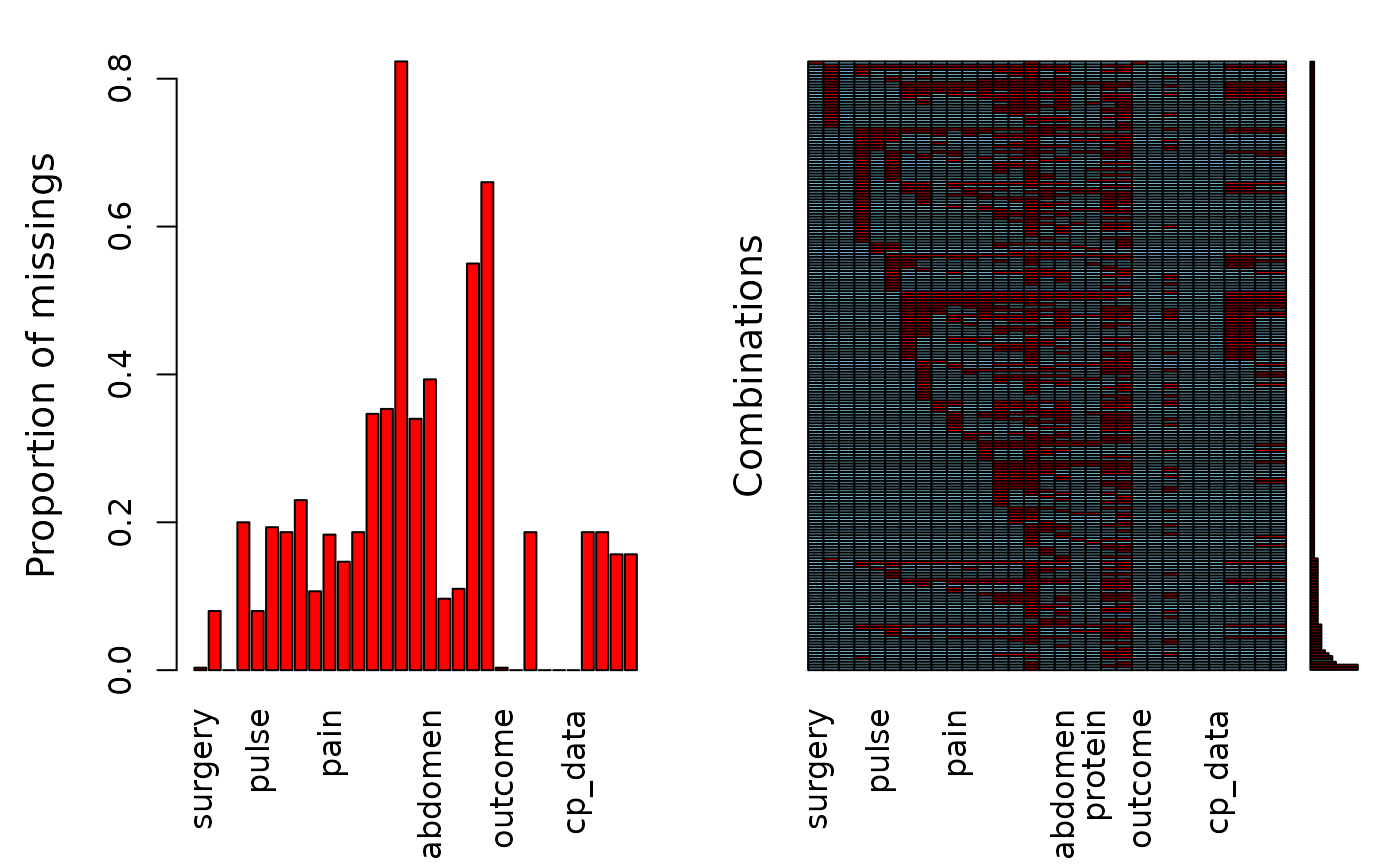
This is a modified version of the original training data set taken from the UCI repository, see reference. The modifications are only related to having appropriate levels for factor variables. This data set is about horse diseases where the task is to determine, if the lesion of the horse was surgical or not.
Format
A training data frame with 300 observations on the following 31 variables.
- surgery
yes or no
- age
1 equals an adult horse, 2 is a horse younger than 6 months
- hospitalID
ID
- temp_rectal
rectal temperature
- pulse
heart rate in beats per minute
- respiratory_rate
a normal rate is between 8 and 10
- temp_extreme
temperature of extremities
- pulse_peripheral
factor with four categories
- capillayr_refill_time
a clinical judgement. The longer the refill, the poorer the circulation. Possible values are 1 = < 3 seconds and 2 = >= 3 seconds
- pain
a subjective judgement of the horse's pain level
- peristalsis
an indication of the activity in the horse's gut. As the gut becomes more distended or the horse becomes more toxic, the activity decreases
- abdominal_distension
An animal with abdominal distension is likely to be painful and have reduced gut motility. A horse with severe abdominal distension is likely to require surgery just tio relieve the pressure
- nasogastric_tube
This refers to any gas coming out of the tube. A large gas cap in the stomach is likely to give the horse discomfort
- nasogastric_reflux
posible values are 1 = none, 2 = > 1 liter, 3 = < 1 liter. The greater amount of reflux, the more likelihood that there is some serious obstruction to the fluid passage from the rest of the intestine
- nasogastric_reflux_PH
scale is from 0 to 14 with 7 being neutral. Normal values are in the 3 to 4 range
- rectal_examination
Rectal examination. Absent feces probably indicates an obstruction
- abdomen
abdomen. possible values 1 = normal, 2 = other, 3 = firm feces in the large intestine, 4 = distended small intestine, 5 = distended large intestine
- cell_volume
packed cell volume. normal range is 30 to 50. The level rises as the circulation becomes compromised or as the animal becomes dehydrated.
- protein
total protein. Normal values lie in the 6-7.5 (gms/dL) range. The higher the value the greater the dehydration
- abdominocentesis_appearance
Abdominocentesis appearance. A needle is put in the horse's abdomen and fluid is obtained from the abdominal cavity
- abdomcentesis_protein
abdomcentesis total protein. The higher the level of protein the more likely it is to have a compromised gut. Values are in gms/dL
- outcome
What eventually happened to the horse?
- surgical_lesion
retrospectively, was the problem (lesion) surgical?
- lesion_type1
type of lesion
- lesion_type2
type of lesion
- lesion_type3
type of lesion
- cp_data
- temp_extreme_ordered
temperature of extremities (ordered)
- mucous_membranes_col
mucous membranes. A subjective measurement of colour
- mucous_membranes_group
different recodings of mucous membrances
Source
https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Horse+Colic Creators: Mary McLeish & Matt Cecile, Department of Computer Science, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada N1G 2W1 Donor: Will Taylor